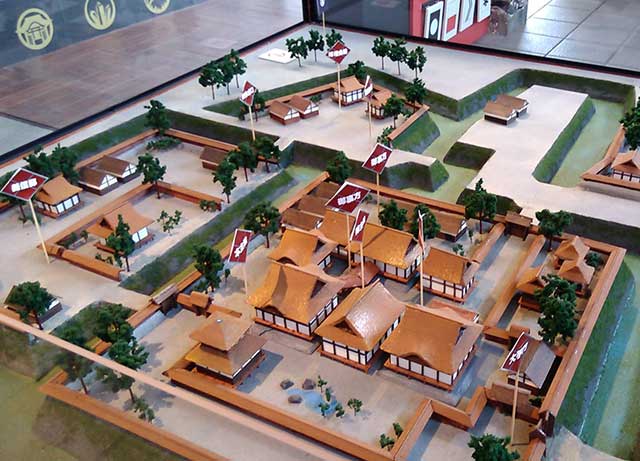

Tsutsujigasaki Castle (Tsutsujigasaki Yakata) served as the fortified residence of the last three generations of the Takeda clan and is located in the heart of Kofu, Yamanashi Prefecture, Japan. Unlike traditional Japanese castles, it was not referred to as a "castle" in Japanese, as the Takeda clan famously believed in relying on their warriors as their true fortifications, stating, "Make men your castle, men your walls, men your moats." Designated a National Historic Site in 1938, the ruins are now open to the public and house the Takeda Shrine, a Shinto shrine dedicated to the deified spirits of the Takeda clan.
The Takeda clan, a cadet branch of the Minamoto clan, gradually gained control of Kai Province during the late Heian period, originally fortifying themselves at Hakusan Castle and Yato Castle. By the Sengoku period, they held the position of shugo (governor) of Kai, and in 1519, Takeda Nobutora chose a central location in the province to establish a fortified residence and castle town. Unlike the common practice of building castles on mountains for defense, Nobutora constructed Tsutsujigasaki on a gentle slope in the Kofu Basin. To compensate for its exposed position, he also built a mountain fortress, Yogaiyama Castle, as a strategic backup stronghold.
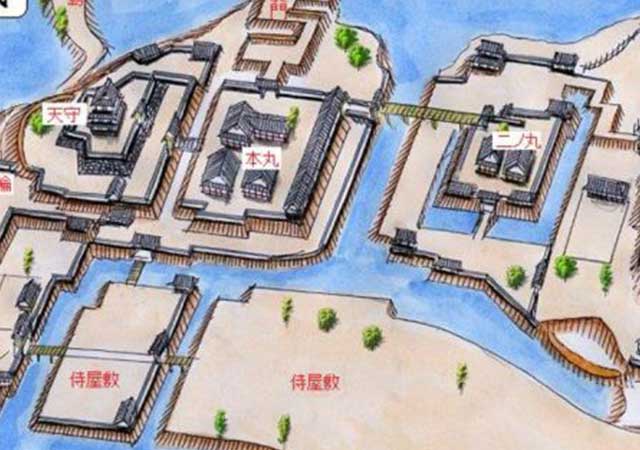
The complex was one of the largest residential fortifications in eastern Japan during the Sengoku period. It featured two main enclosures surrounded by a combination of flooded and dry moats. The central enclosure housed the Takeda ruler’s private residence, while the western enclosure served as the administrative center, featuring heavily fortified "umadashi"-style gates. Additionally, two secondary enclosures, Miso-guruwa and Baio-guruwa, provided extra layers of defense. Today, the site retains some of its original water moats and minor stonework, with the Takeda Shrine, built in 1919, standing at its center. A museum, guarded by a stone Hello Kitty, is located to the right of the shrine.
Tsutsujigasaki remained Takeda Shingen’s primary residence after he overthrew his father in 1540. However, in 1581, his son, Takeda Katsuyori, moved to the newly constructed Shinpu Castle in Nirasaki. The Takeda clan met its downfall in 1582 when it was annihilated by the combined forces of Oda Nobunaga and Tokugawa Ieyasu. Following this, Nobunaga's general, Kawajiri Hidetaka, briefly ruled Kai Province from Tsutsujigasaki until Nobunaga’s assassination later that year. With the completion of Kofu Castle in 1594, Tsutsujigasaki was ultimately abandoned.
See also
-
Sawayama Castle
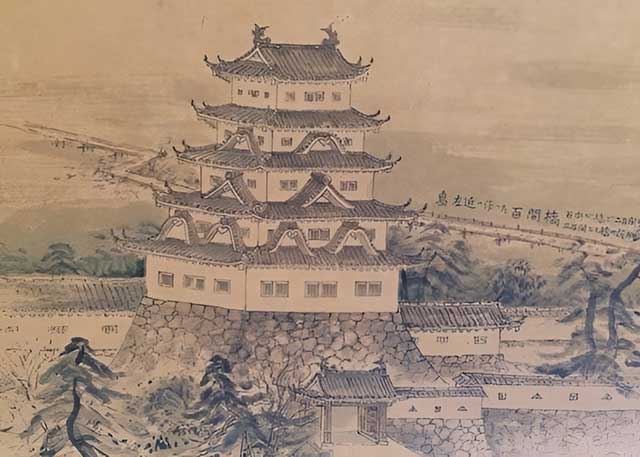

During the Kamakura period, Sabo Tokitsuna, the sixth son of Sasaki Sadatsuna, built a fort on Mount Sawayama. This fort occupied a strategically important position because it allowed control over traffic along the important Tōsandō route, which was later known as Nakasendō. This road connected the capital, Kyoto, with the eastern regions of the country. Due to its location, the fortification held great military importance, and during periods of civil war it repeatedly became the site of fierce battles.
-
Nadzima Castle
It is believed that the first structures on this site were built by Tachibana Akitoshi (?-1568), head of the Tachibana clan, a branch family of the Ōtomo clan, as auxiliary fortifications for Tachibanayama Castle. In 1587, Toyotomi Hideyoshi established control over the island of Kyushu and granted Chikuzen Province to Kobayakawa Takakage, one of the leading vassals of the Mori clan. Takakage began construction of a new castle on the site of the existing fortifications in 1588. The exact date of completion is unknown, but by the time the invasion of Korea began in 1592, the castle had already been finished, as records note that Toyotomi Hideyoshi stayed there overnight on his way to Hizen Nagoya Castle, which served as the headquarters of the invasion forces.
-
Kubota Castle
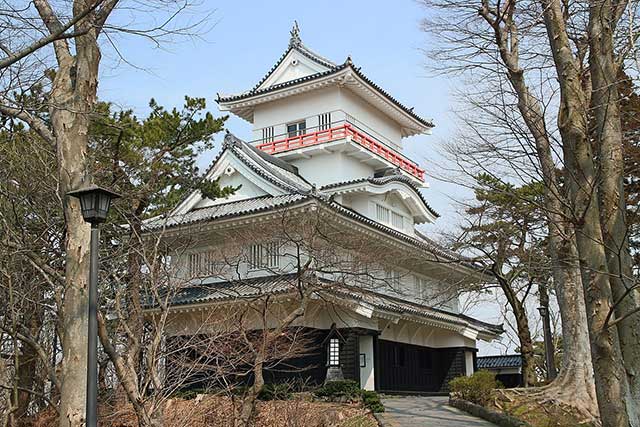

The founder of the castle is considered to be Satake Yoshinobu (1570–1633). Yoshinobu was one of the six great generals of Toyotomi Hideyoshi. During the Odawara Campaign of 1590, he took part in the siege of Oshi Castle under the command of Ishida Mitsunari, with whom Yoshinobu developed a good relationship.
-
Kavanhoe Castle
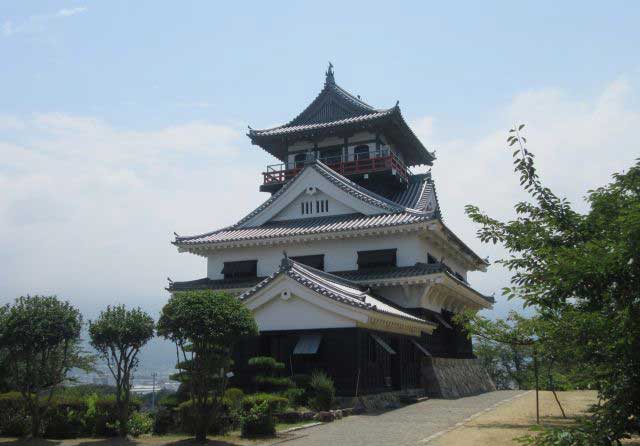

Kawanoe Castle is located on the small Wasi-yama hill near the port area of the Kawanoe district in the city of Shikokuchuo, occupying a central position along the northern coast of Shikoku Island. Kawanoe was also known as Butsuden Castle. The term “butsuden” in Japan refers to temple halls, and for this reason it is believed that a Buddhist temple once stood on the site before the castle was built. Due to its location at the junction of four provinces on Shikoku Island, Kawanoe held significant strategic importance and was repeatedly targeted by rival forces seeking military control over the region.
-
Yokote Castle
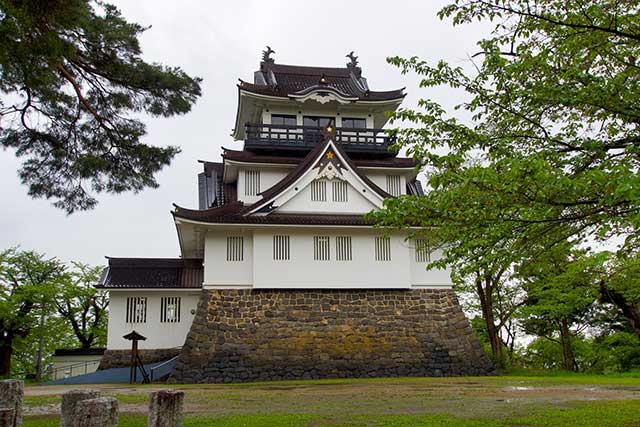

The founder of the castle is considered to be the Onodera clan. The Onodera were originally a minor clan from Shimotsuke Province and served Minamoto no Yoritomo (1147–1199), the founder of the first shogunate. The Onodera distinguished themselves in battle against the Fujiwara clan of the Ōshū branch and were rewarded with lands around Yokote. Around the 14th century, the Onodera moved to Yokote as their permanent residence. Their original stronghold was Numadate Castle, but after a series of clashes with the powerful Nambu clan, they relocated their base to the site of present-day Yokote Castle. It was likely during this time that the first fortifications appeared at the castle.
-
Wakayama Castle
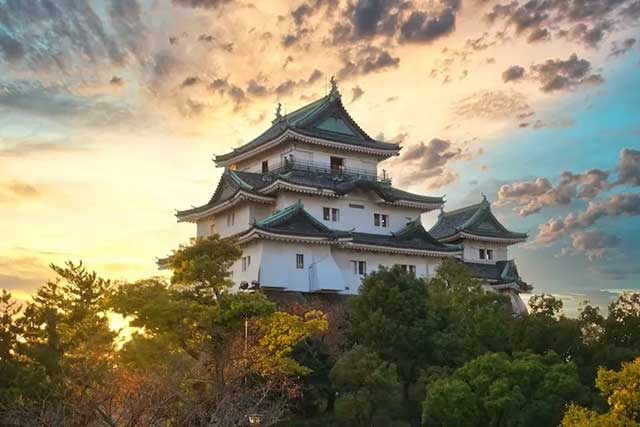

Wakayama Castle was built in 1585, when Toyotomi Hideyoshi ordered his uterine brother, Hashiba (Toyotomi) Hidenaga, to construct a castle on the site of the recently captured Ota Castle. The purpose of this construction was to secure control over the likewise newly conquered Province of Kii. Following an already established tradition, Hidenaga entrusted the project to his castle-building expert, Todo Takatora. Takatora carefully inspected the future castle site, personally drew up several designs, created a model of the planned castle, and took part in the work of laying out the grounds (nawabari). For the construction he brought in more than 10,000 workers and completed the large-scale project within a single year, which was considered extremely fast by the standards of the time.
Toyama Castle
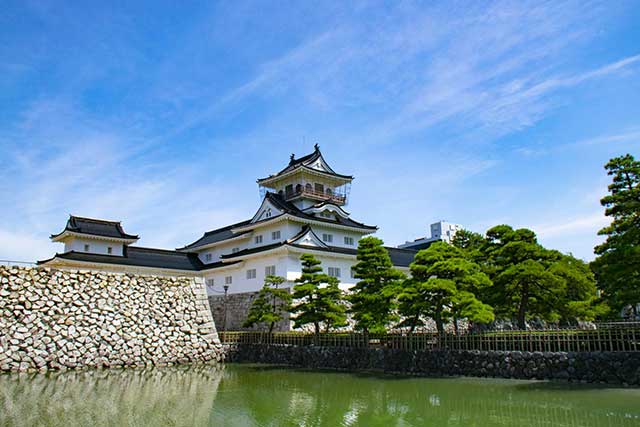

Toyama Castle is located almost in the very center of the former province of Etchū and is surrounded by a wide plain with a large number of rivers. The very first castle on the banks of the Jinzu River was built in 1543 by Jimbo Nagamoto. The Jimbo clan were vassals of the Hatakeyama clan and governed the western part of Etchū Province. The eastern part of the province belonged to their rivals, the Shiina clan, who were also Hatakeyama vassals. Beginning in the 15th century, the influence of the ancient Hatakeyama clan gradually weakened, and as a result, the Jimbo and the Shiina fought constant wars for control of the province. Meanwhile, the forces of the Ikkō-ikki movement periodically intervened, helping first one side and then the other.
Takada Castle
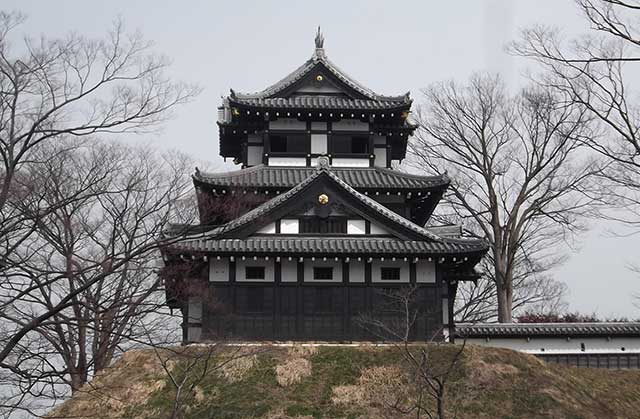

During the Sengoku period, the lands where Takada Castle would later be built were part of Echigo Province and were controlled by the Uesugi clan.

