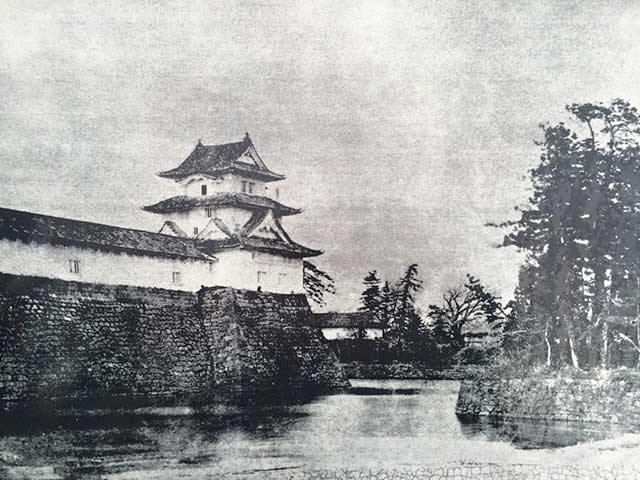

Fukui Castle, erected in 1606 by Yuki Hideyasu, Tokugawa Ieyasu's clandestine son, stands as a testament to a complex family history. Born to Oman, a servant of Ieyasu's wife Tsukiyama Dono, Yuki Hideyasu was concealed by his father out of fear of marital discord. Raised in the shadows until his emergence as a samurai, Yuki proved his mettle in numerous battles, earning accolades from Ieyasu himself.
At the pivotal Battle of Sekigahara, Yuki Hideyasu sided with his father's Eastern forces, showcasing his prowess once more and garnering Ieyasu's admiration. In recognition of his valor, Ieyasu granted him the lands of Shibata Katsuie in Echizen Province (now Fukui Prefecture) and aided in the construction of Fukui Castle. Designed by Ieyasu and fortified with stones from Kitanosho Castle, the castle complex, including the Honmaru and Ni-no-maru precincts, took six years to complete.
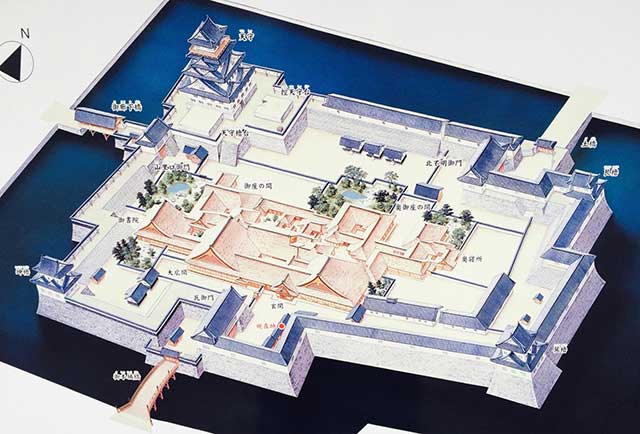
In 1624, Fukui Castle was formally christened by its third lord, Matsudaira Tadamasa, marking the beginning of Fukui Domain's rule under the Matsudaira clan for 270 years. Although the castle's iconic five-story tower keep succumbed to flames in 1669 and was never rebuilt, the resilient stone walls and expansive moats endure as silent witnesses to centuries of history.
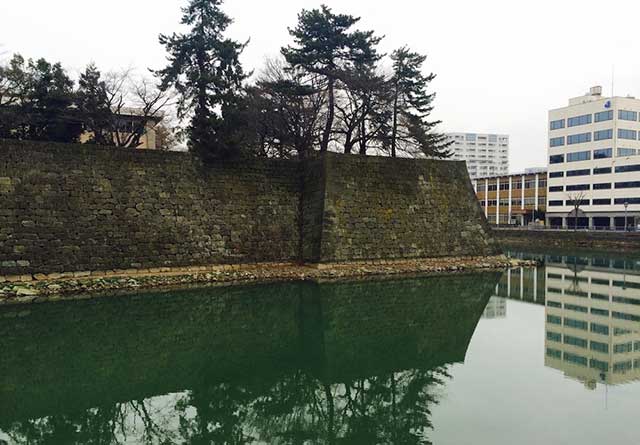

Today, the former castle grounds host governmental and law enforcement offices, yet echoes of Fukui Castle's legacy persist. A monumental stone statue of Yuki Hideyasu graces the landscape, while ongoing efforts seek to enhance the site's historical authenticity, including the restoration of strategic gates like the Rokabashi bridge and the Yamazato-guchi Gomon Gate. The castle's original stone base remains accessible to the public, offering a glimpse into Fukui's storied past amidst the modernity of Fukui Prefecture.
Siehe auch
-
Kubota Castle

The founder of the castle is considered to be Satake Yoshinobu (1570–1633). Yoshinobu was one of the six great generals of Toyotomi Hideyoshi. During the Odawara Campaign of 1590, he took part in the siege of Oshi Castle under the command of Ishida Mitsunari, with whom Yoshinobu developed a good relationship.
-
Kavanhoe Castle
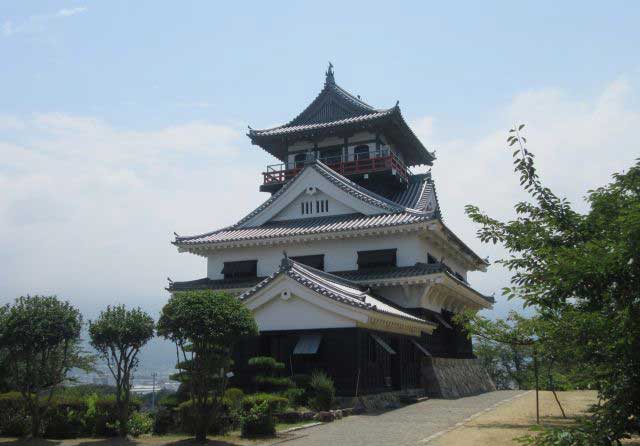

Kawanoe Castle is located on the small Wasi-yama hill near the port area of the Kawanoe district in the city of Shikokuchuo, occupying a central position along the northern coast of Shikoku Island. Kawanoe was also known as Butsuden Castle. The term “butsuden” in Japan refers to temple halls, and for this reason it is believed that a Buddhist temple once stood on the site before the castle was built. Due to its location at the junction of four provinces on Shikoku Island, Kawanoe held significant strategic importance and was repeatedly targeted by rival forces seeking military control over the region.
-
Yokote Castle
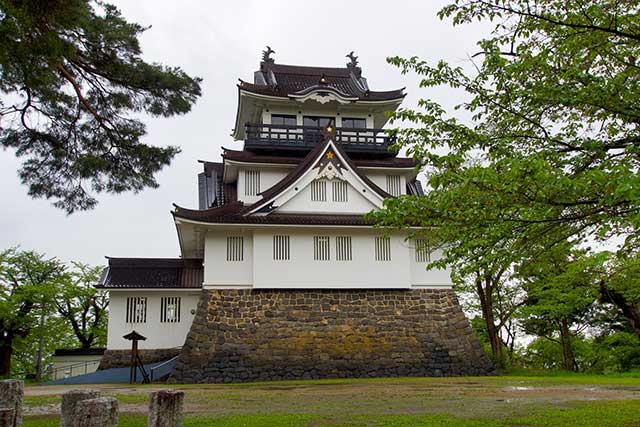

The founder of the castle is considered to be the Onodera clan. The Onodera were originally a minor clan from Shimotsuke Province and served Minamoto no Yoritomo (1147–1199), the founder of the first shogunate. The Onodera distinguished themselves in battle against the Fujiwara clan of the Ōshū branch and were rewarded with lands around Yokote. Around the 14th century, the Onodera moved to Yokote as their permanent residence. Their original stronghold was Numadate Castle, but after a series of clashes with the powerful Nambu clan, they relocated their base to the site of present-day Yokote Castle. It was likely during this time that the first fortifications appeared at the castle.
-
Wakayama Castle
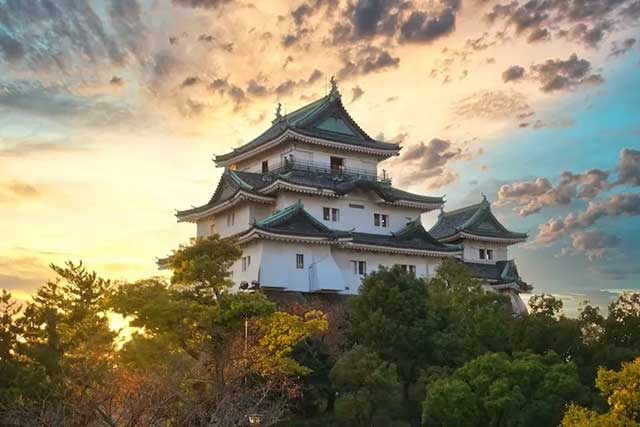

Wakayama Castle was built in 1585, when Toyotomi Hideyoshi ordered his uterine brother, Hashiba (Toyotomi) Hidenaga, to construct a castle on the site of the recently captured Ota Castle. The purpose of this construction was to secure control over the likewise newly conquered Province of Kii. Following an already established tradition, Hidenaga entrusted the project to his castle-building expert, Todo Takatora. Takatora carefully inspected the future castle site, personally drew up several designs, created a model of the planned castle, and took part in the work of laying out the grounds (nawabari). For the construction he brought in more than 10,000 workers and completed the large-scale project within a single year, which was considered extremely fast by the standards of the time.
Toyama Castle
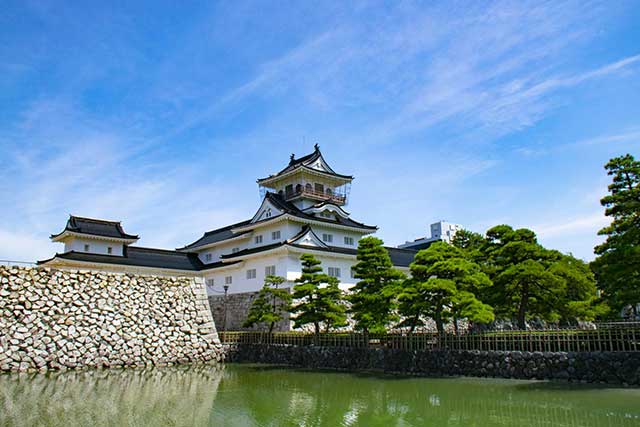

Toyama Castle is located almost in the very center of the former province of Etchū and is surrounded by a wide plain with a large number of rivers. The very first castle on the banks of the Jinzu River was built in 1543 by Jimbo Nagamoto. The Jimbo clan were vassals of the Hatakeyama clan and governed the western part of Etchū Province. The eastern part of the province belonged to their rivals, the Shiina clan, who were also Hatakeyama vassals. Beginning in the 15th century, the influence of the ancient Hatakeyama clan gradually weakened, and as a result, the Jimbo and the Shiina fought constant wars for control of the province. Meanwhile, the forces of the Ikkō-ikki movement periodically intervened, helping first one side and then the other.
Takada Castle
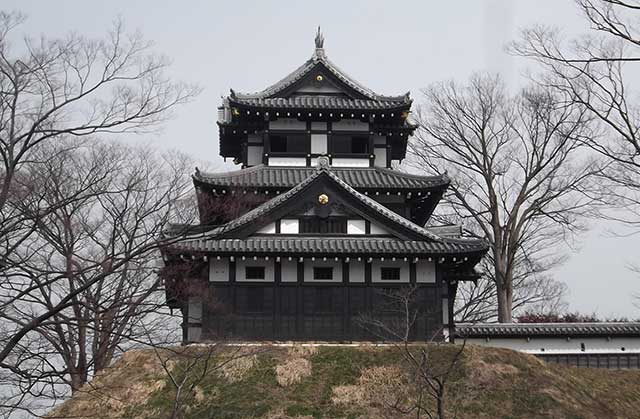

During the Sengoku period, the lands where Takada Castle would later be built were part of Echigo Province and were controlled by the Uesugi clan.
Kishiwada Castle
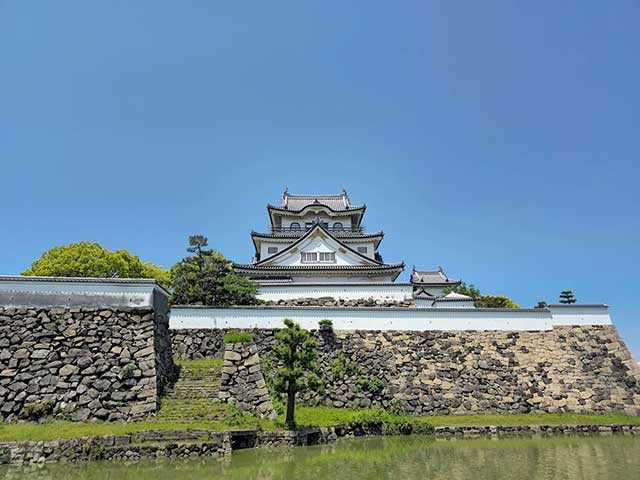

The celebrated 14th-century military commander Kusunoki Masashige (1294–1336), who owned extensive lands south of what is now the city of Osaka, ordered one of his vassals, Kishiwada Osamu, to build a fortified residence. This order was carried out around 1336. These fortifications became the first structures on the site of what would later become Kishiwada Castle. From the beginning, the castle stood in a strategically important location—roughly halfway between the cities of Wakayama and Osaka, south of the key port of Sakai. Because of this position, it changed hands several times during periods of warfare.
Kaminoyama Castle
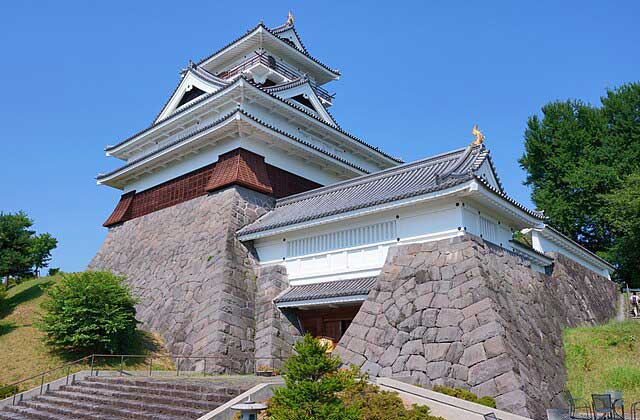

Kamino-yama Castle stood at the center of an important logistics hub, in the middle of the Yonezawa Plain, which served as the gateway to the western part of the Tohoku region. Roads connecting the Aizu, Fukushima, and Yamagata areas intersected here.

