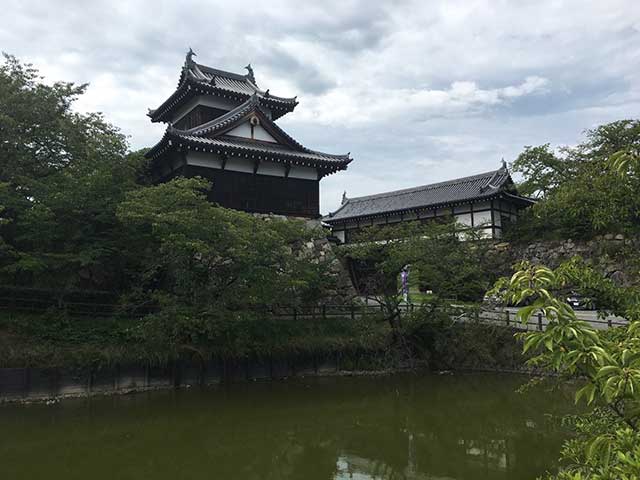

The impressive ruins of Koriyama Castle sit atop a small hill, surrounded by two rivers. The strategic positioning and strong layout of the castle served it well through the final years of the Sengoku period and the peaceful days of the Edo period.
Tsutsui Junkei (1549-1584), after defeating Matsunaga Hisahide with the assistance of Oda Nobunaga, relocated from Tsutsui Castle to Koriyama and built the magnificent castle as a symbol of his mastery over the Yamato region. Two years after its completion in 1580, Akechi Mitsuhide attacked Oda Nobunaga in the Honno-ji Incident and sought Tsutsui’s military assistance at Horagatoge Pass. Tsutsui, who had served under Akechi since allying with the Oda, hesitated and observed the unfolding events before deciding his course of action. This delayed response led to the Japanese saying “Horagatoge wo kimekomu,” meaning “to wait and see what happens at Horagatoge,” used sarcastically to describe someone who waits to join the winning side.
In 1595, Mashita Nagamori ruled the area from the fine castle but was forced out following the Battle of Sekigahara in 1600. For the next 15 years, Koriyama remained vacant until the Tokugawa installed Mizuno Katsushige in Yamato, tasking him with reconstructing the now-dilapidated structures. The Honda clan also served as lords of Koriyama.
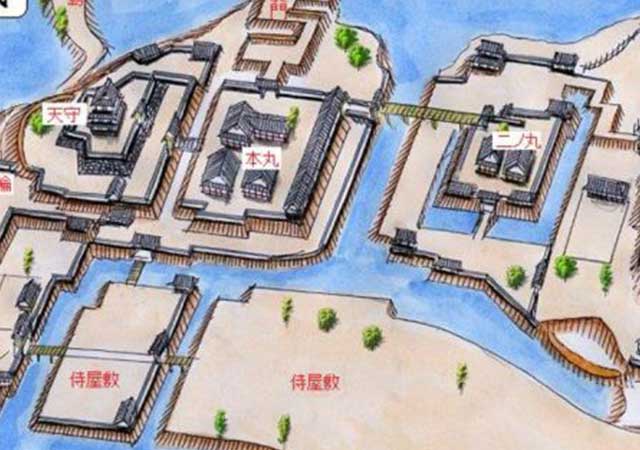
In 1724, the Yanagisawa clan of Kofu (Yamanashi Prefecture) became masters of Koriyama. Upon hearing of Lord Yanagisawa Yoshisato’s transfer, the peasants of Kofu promptly paid their annual rice tax and saw their lord off with respect. He brought with him 5,286 retainers and their families to Koriyama, along with his prized pet goldfish. This led to a prosperous side business for many lower-ranked samurai, sustaining them long after the Meiji Restoration in 1868, when the samurai were disbanded. The Yanagisawa clan also introduced silkworm farming, improving the local economy. They remained in control of Koriyama until the Meiji Restoration. Koriyama Castle was destroyed in 1873. The surrounding deep moats, impressive stonework, and the castle’s Rinkakushiki layout, with the Honmaru protected on all four sides by surrounding baileys and precincts, offer much for castle enthusiasts to enjoy. Having been built in 1580, the stone walls exhibit a mixture of stoneworking methods.
The Otemon gate, Ote Mukai Yagura, Tamon Yagura, and Ote East Yagura have been well reconstructed and are open at certain times during the year. Plans are underway to reconstruct the Gokuraku Bridge and Hakutaku gate. Koriyama Castle was designated one of the Alternative Top 100 Castles in early 2017.
See also
-
Nadzima Castle
It is believed that the first structures on this site were built by Tachibana Akitoshi (?-1568), head of the Tachibana clan, a branch family of the Ōtomo clan, as auxiliary fortifications for Tachibanayama Castle. In 1587, Toyotomi Hideyoshi established control over the island of Kyushu and granted Chikuzen Province to Kobayakawa Takakage, one of the leading vassals of the Mori clan. Takakage began construction of a new castle on the site of the existing fortifications in 1588. The exact date of completion is unknown, but by the time the invasion of Korea began in 1592, the castle had already been finished, as records note that Toyotomi Hideyoshi stayed there overnight on his way to Hizen Nagoya Castle, which served as the headquarters of the invasion forces.
-
Kubota Castle
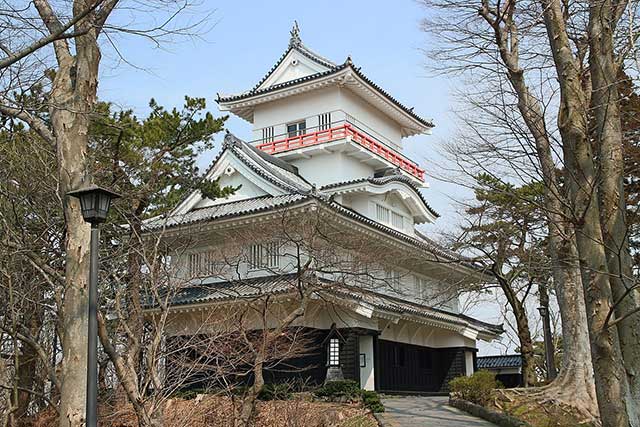

The founder of the castle is considered to be Satake Yoshinobu (1570–1633). Yoshinobu was one of the six great generals of Toyotomi Hideyoshi. During the Odawara Campaign of 1590, he took part in the siege of Oshi Castle under the command of Ishida Mitsunari, with whom Yoshinobu developed a good relationship.
-
Kavanhoe Castle
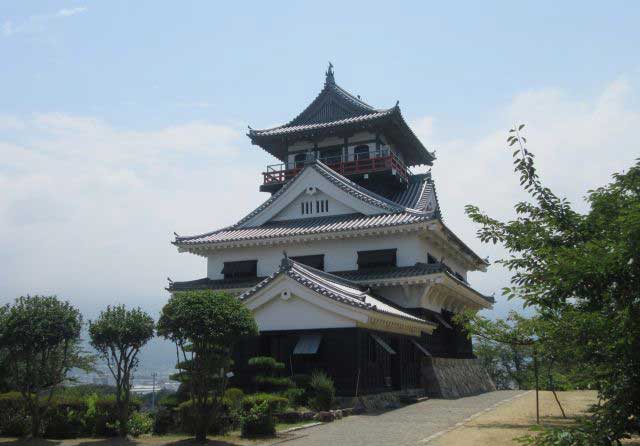

Kawanoe Castle is located on the small Wasi-yama hill near the port area of the Kawanoe district in the city of Shikokuchuo, occupying a central position along the northern coast of Shikoku Island. Kawanoe was also known as Butsuden Castle. The term “butsuden” in Japan refers to temple halls, and for this reason it is believed that a Buddhist temple once stood on the site before the castle was built. Due to its location at the junction of four provinces on Shikoku Island, Kawanoe held significant strategic importance and was repeatedly targeted by rival forces seeking military control over the region.
-
Yokote Castle
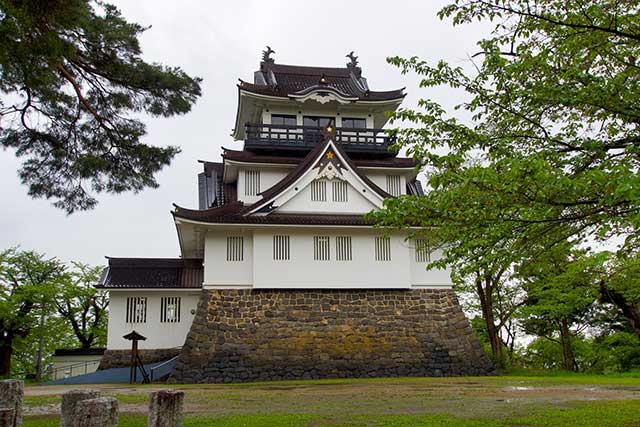

The founder of the castle is considered to be the Onodera clan. The Onodera were originally a minor clan from Shimotsuke Province and served Minamoto no Yoritomo (1147–1199), the founder of the first shogunate. The Onodera distinguished themselves in battle against the Fujiwara clan of the Ōshū branch and were rewarded with lands around Yokote. Around the 14th century, the Onodera moved to Yokote as their permanent residence. Their original stronghold was Numadate Castle, but after a series of clashes with the powerful Nambu clan, they relocated their base to the site of present-day Yokote Castle. It was likely during this time that the first fortifications appeared at the castle.
-
Wakayama Castle
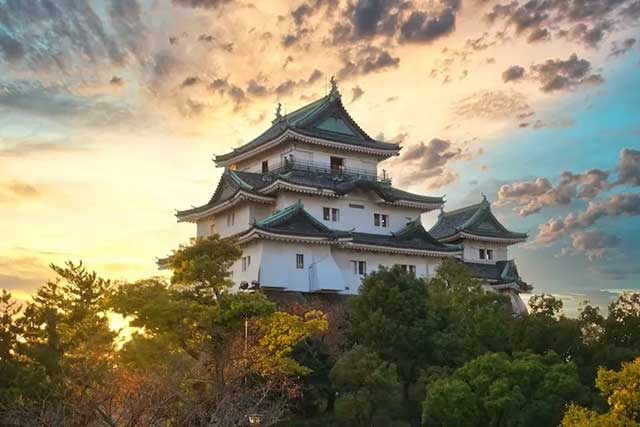

Wakayama Castle was built in 1585, when Toyotomi Hideyoshi ordered his uterine brother, Hashiba (Toyotomi) Hidenaga, to construct a castle on the site of the recently captured Ota Castle. The purpose of this construction was to secure control over the likewise newly conquered Province of Kii. Following an already established tradition, Hidenaga entrusted the project to his castle-building expert, Todo Takatora. Takatora carefully inspected the future castle site, personally drew up several designs, created a model of the planned castle, and took part in the work of laying out the grounds (nawabari). For the construction he brought in more than 10,000 workers and completed the large-scale project within a single year, which was considered extremely fast by the standards of the time.
Toyama Castle
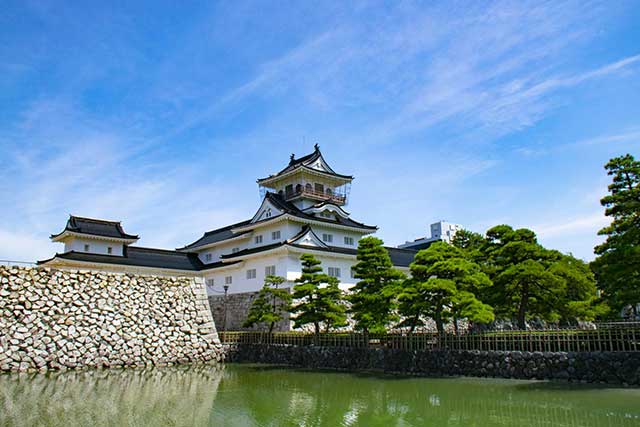

Toyama Castle is located almost in the very center of the former province of Etchū and is surrounded by a wide plain with a large number of rivers. The very first castle on the banks of the Jinzu River was built in 1543 by Jimbo Nagamoto. The Jimbo clan were vassals of the Hatakeyama clan and governed the western part of Etchū Province. The eastern part of the province belonged to their rivals, the Shiina clan, who were also Hatakeyama vassals. Beginning in the 15th century, the influence of the ancient Hatakeyama clan gradually weakened, and as a result, the Jimbo and the Shiina fought constant wars for control of the province. Meanwhile, the forces of the Ikkō-ikki movement periodically intervened, helping first one side and then the other.
Takada Castle
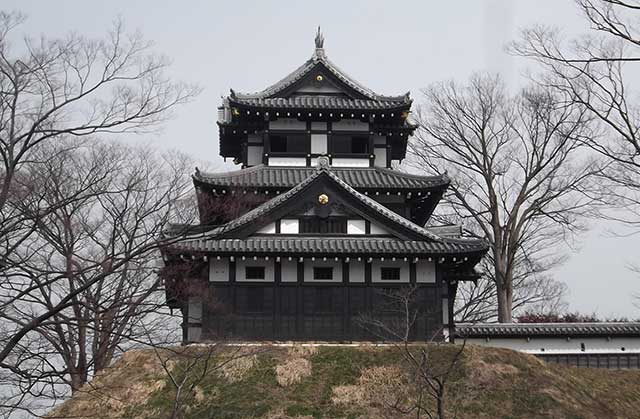

During the Sengoku period, the lands where Takada Castle would later be built were part of Echigo Province and were controlled by the Uesugi clan.
Kishiwada Castle
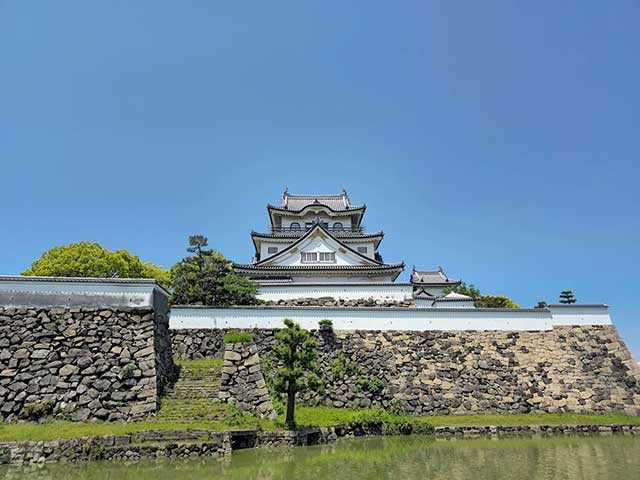

The celebrated 14th-century military commander Kusunoki Masashige (1294–1336), who owned extensive lands south of what is now the city of Osaka, ordered one of his vassals, Kishiwada Osamu, to build a fortified residence. This order was carried out around 1336. These fortifications became the first structures on the site of what would later become Kishiwada Castle. From the beginning, the castle stood in a strategically important location—roughly halfway between the cities of Wakayama and Osaka, south of the key port of Sakai. Because of this position, it changed hands several times during periods of warfare.

